Book Appointment Now

The Science of Rhythm: How Drumming Improves Your Brain and Body
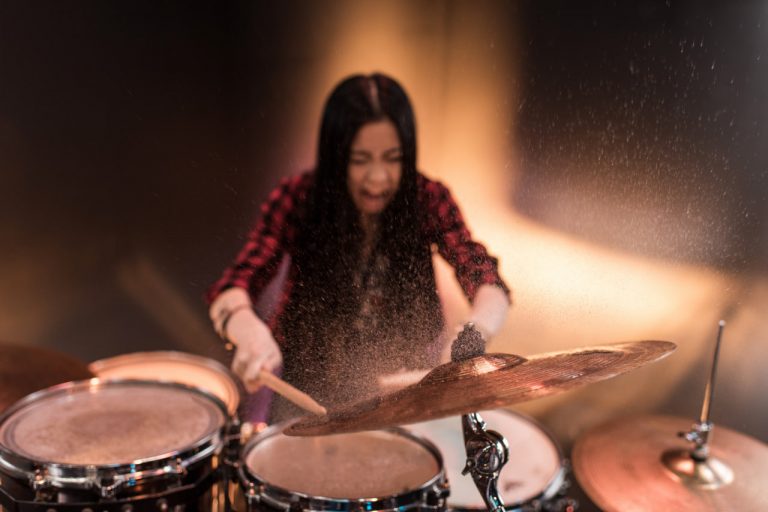
Drumming is often seen as pure energy, creativity, and entertainment, but science reveals that it is much more than that. Behind every beat lies a fascinating connection between rhythm, the brain, and the body. Research has shown that drumming is not only a musical skill but also a powerful tool for improving mental and physical health. From boosting cognitive abilities to reducing stress and enhancing coordination, drumming engages the mind and body in ways that few other activities can.
Drumming and Brain Function
When you play drums, multiple parts of the brain are activated simultaneously. Unlike many other instruments that focus on melody or harmony, drumming demands rhythm, timing, and physical coordination. Studies using brain scans have shown that drumming increases activity in both the left and right hemispheres, strengthening the communication between them.
This kind of cross-hemisphere activity is linked to better problem-solving skills, improved memory, and enhanced creativity. Playing complex rhythms also challenges the brain’s ability to process patterns, which sharpens focus and trains the brain to think in structured but flexible ways.
The Role of Rhythm in Stress Relief
One of the most immediate benefits drumming provides is stress reduction. The physical act of striking drums is a natural release of energy and tension, while the steady rhythm helps regulate breathing and heart rate. This creates a meditative effect, similar to mindfulness practices, where the body and mind synchronize with the beat.
Research in music therapy has shown that drumming can lower cortisol levels, the hormone responsible for stress, and promote the release of endorphins, which improve mood and create a sense of well-being. Group drumming sessions in particular enhance these effects, combining music with social bonding and collective energy.
Drumming and Physical Coordination
Drumming is a full-body workout disguised as music. It requires the hands, feet, and sometimes even the voice to work in coordination, all while maintaining consistent timing. This improves motor skills, reflexes, and muscle memory.
Regular practice builds endurance, strengthens the arms and legs, and enhances overall physical agility. Unlike repetitive exercise routines, drumming keeps the body active through constant variation in movement, making it both challenging and enjoyable.
Cognitive Benefits of Rhythm Training
Learning to keep time, switch between grooves, and master complex patterns develops strong cognitive control. Drummers often show superior multitasking abilities because they are used to managing several actions at once — for example, keeping a steady hi-hat rhythm with the foot while playing syncopated snare hits and bass drum kicks.
This mental workout extends beyond music. It can improve focus at school, productivity at work, and even memory retention. For children and teenagers, drumming supports brain development, while for adults it helps maintain mental sharpness over time.
Rhythm as a Universal Language
Beyond science, rhythm has always been central to human culture. From ancient tribal rituals to modern concerts, drumming has connected people, creating shared experiences that transcend language and background. This social aspect stimulates empathy, teamwork, and a sense of belonging, all of which contribute to mental and emotional health.